Personality Disorders
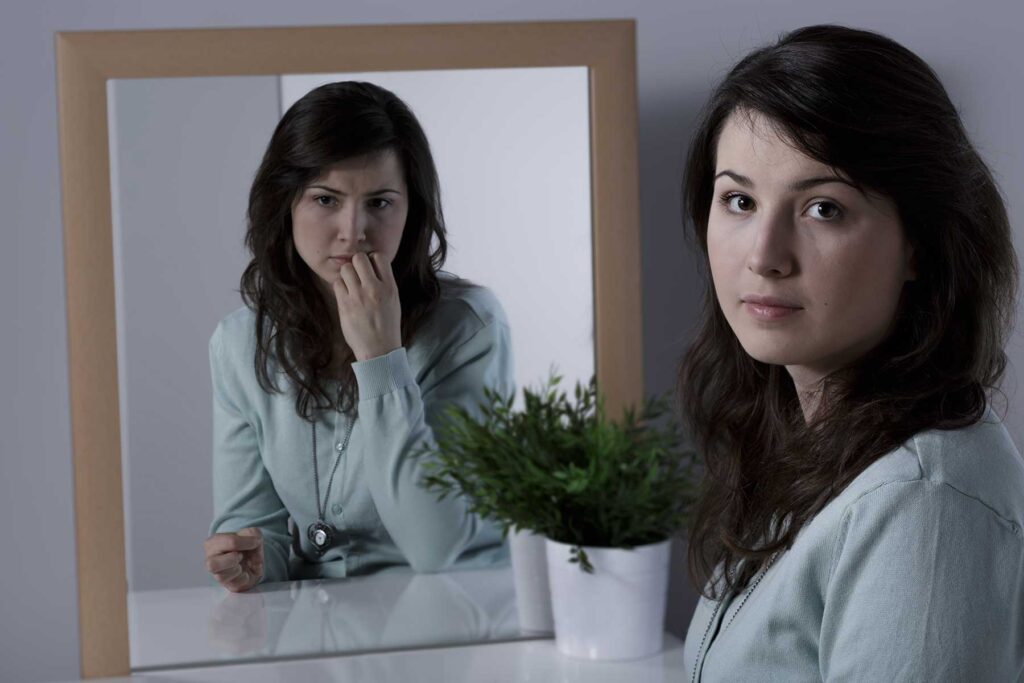
A personality disorder is a mental health condition that involves long-lasting, all-encompassing, disruptive patterns of thinking, behavior, mood and relating to others. These patterns cause a person significant distress and/or impair their ability to function.
There are 10 types of personality disorders, each with different characteristics and symptoms.
Personality is vital to defining who we are as individuals. It involves a unique blend of traits — including attitudes, thoughts and behaviors — as well as how we express these traits in our interactions with others and with the world around us.
Personality disorders may cause distorted perceptions of reality, abnormal behaviors and distress across various aspects of life, including work, relationships and social functioning. Additionally, people with a personality disorder may not recognize their troubling behaviors or the negative effect they have on others.
Who do personality disorders affect?
Anyone can have a personality disorder. But different types of personality disorders affect people differently.
Most personality disorders begin in the teen years when your personality further develops and matures. As a result, almost all people diagnosed with personality disorders are above the age of 18. One exception to this is antisocial personality disorder — approximately 80% of people with this disorder will have started to show symptoms by the age of 11.
Antisocial personality disorders are more likely to affect people assigned male at birth. Borderline, histrionic and dependent personality disorders are more likely to affect people assigned female at birth.
Symptoms and Causes
Anyone can have a personality disorder. But different types of personality disorders affect people differently.
Most personality disorders begin in the teen years when your personality further develops and matures. As a result, almost all people diagnosed with personality disorders are above the age of 18. One exception to this is antisocial personality disorder — approximately 80% of people with this disorder will have started to show symptoms by the age of 11.
Antisocial personality disorders are more likely to affect people assigned male at birth. Borderline, histrionic and dependent personality disorders are more likely to affect people assigned female at birth.
What causes personality disorders?
Personality disorders are among the least understood mental health conditions. Scientists are still trying to figure out the cause of them.
So far, they believe the following factors may contribute to the development of personality disorders:
- Genetics: Scientists have identified a malfunctioning gene that may be a factor in obsessive-compulsive personality disorder. Researchers are also exploring genetic links to aggression, anxiety and fear, which are traits that can play a role in personality disorders.
- Brain changes: Researchers have identified subtle brain differences in people with certain personality disorders. For example, findings in studies on paranoid personality disorder point to altered amygdala functioning. The amygdala is the part of your brain that’s involved with processing fearful and threatening stimuli. In a study on schizotypal personality disorder, researchers found a volumetric decrease in the frontal lobe of their brain.
- Childhood trauma: One study revealed a link between childhood traumas and the development of personality disorders. People with borderline personality disorder, for example, had especially high rates of childhood sexual trauma. People with borderline and antisocial personality disorders have issues with intimacy and trust, both of which may be related to childhood abuse and trauma.
- Verbal abuse: In one study, people who experienced verbal abuse as children were three times as likely to have borderline, narcissistic, obsessive-compulsive or paranoid personality disorders in adulthood.
- Cultural factors: Cultural factors may also play a role in the development of personality disorders, as demonstrated by the varying rates of personality disorders between different countries. For example, there are remarkably low cases of antisocial personality disorders in Taiwan, China and Japan, along with significantly higher rates of cluster C personality disorders.
What are the symptoms of personality disorders?
Each of the 10 types of personality disorders has its own specific signs and symptoms.
But, in general, personality disorders involve problems with:
- Identity and a sense of self: People with a personality disorder generally lack a clear or stable image of themselves, and how they see themselves often changes depending on the situation or the people they’re with. Their self-esteem may be unrealistically high or low.
- Relationships: People with a personality disorder struggle to form close, stable relationships with others due to their problematic beliefs and behaviors. They may lack empathy or respect for others, be emotionally detached or be overly needy of attention and care.
Another distinguishing sign of personality disorders is that most people who have one often have little to no insight or self-awareness of how their thoughts and behaviors are problematic.
How are personality disorders diagnosed?
When a mental health professional, like a psychologist or psychiatrist, suspects someone might have a personality disorder, they often ask broad, general questions that won’t create a defensive response or hostile environment. They ask questions that will shed light on:
- Past history.
- Relationships
- Previous work history.
- Reality testing.
- Impulse control.
Because a person suspected of having a personality disorder may lack insight into their behaviors, mental health professionals often work with the person’s family, friends and/or parole officers to collect more insight about their behaviors and history.
Personality disorders are generally underdiagnosed because providers sometimes focus on the symptoms of anxiety or depression, which are much more common in the general population than personality disorders. These symptoms may overshadow the features of any underlying personality disorder.